
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1832 Arabic Præsidentvalget i USA 1832 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1832 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1832 Spanish انتخابات ریاستجمهوری ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۸۳۲) Persian Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1832 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1832 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1832 HE Elezioni presidenziali negli Stati Uniti d'America del 1832 Italian 1832年アメリカ合衆国大統領選挙 Japanese
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
288 members of the Electoral College[a] 145 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 57%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
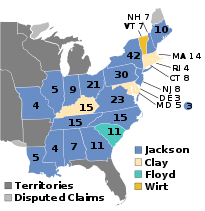 Presidential election results map. Blue denotes states won by Jackson and Van Buren or Wilkins, Astra denotes those won by Clay/Sergeant, Teal denotes those won by Floyd/Lee, and Gold denotes those won by Wirt/Ellmaker. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. Two votes were not given in Maryland. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1832 United States presidential election was the 12th quadrennial presidential election, held from Friday, November 2 to Wednesday, December 5, 1832. Incumbent president Andrew Jackson, candidate of the Democratic Party, defeated Henry Clay, candidate of the National Republican Party.
The election saw the first use of the presidential nominating conventions, and the Democrats, National Republicans, and the Anti-Masonic Party all used conventions to select their candidates. Jackson won re-nomination with no opposition, and the 1832 Democratic National Convention replaced Vice President John C. Calhoun with Martin Van Buren. The National Republican Convention nominated a ticket led by Clay, a Kentuckian who had served as Secretary of State under President John Quincy Adams. The Anti-Masonic Party, one of the first major U.S. third parties, nominated former Attorney General William Wirt.
Jackson faced heavy criticism for his actions in the Bank War, but remained popular among the general public. He won a majority of the popular vote and 219 of the 288 electoral votes, carrying most states outside New England. Clay won 37.4% of the popular vote and 49 electoral votes, while Wirt won 7.8% of the popular vote and carried the state of Vermont. Virginia Governor John Floyd, who had not actively campaigned, won South Carolina's electoral votes. After the election, members of the National Republican Party and the Anti-Masonic Party formed the Whig Party, which became the Democrats' primary opponent over the next two decades.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search



